![Micro Teaching | Micro Teaching Skills | MicroTeaching [Everything You Need To Know] micro teaching micro teaching skills skills of micro teaching skills in micro teaching skill of micro teaching, what micro teaching, micro teaching hindi, what is micro teaching, definition of micro teaching, micro teaching ppt, micro teaching pdf, components of micro teaching, principles of micro teaching, micro teaching cycle, steps of micro teaching, concept of micro teaching, types of micro teaching, micro teaching definition, micro teaching lesson plan, micro teaching skills pdf, micro teaching skills illustrating with examples, advantages of micro teaching, characteristics of micro teaching, importance of micro teaching, define micro teaching, disadvantages of micro teaching, objectives of micro teaching, microteaching, skills of microteaching, microteaching definition, microteaching cycle, steps of microteaching, microteaching ppt, microteaching lesson plans, microteaching lesson plan, phases of microteaching, microteaching pdf, microteaching presentation, phases of microteaching pdf, skill of questioning in microteaching, importance of microteaching, define microteaching, advantages of microteaching, introduction skill in microteaching, introduction skill in microteaching ppt,](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEikMP8pzIgCUspk4aPRX8T3-gDmFN5KgZJHWpCfUTksBl99U3jEM5QGWNgbnbgLMv3E6qW07Ml9fIBEFjwypDcwYTR9irBVnnJZIUdXE-MpyycW4QCgfgu6wNv9NDf-M_1aTWad8DpagMI/s16000/micro-teaching-www.learningclassesonline.com.png)
Table of Contents
- Concept and Introduction to Micro Teaching?
- Meaning of Micro Teaching
- Definition of Micro Teaching
- What are the Objectives of Micro Teaching?
- Characteristics and Features of Micro Teaching
- Steps of Micro Teaching
- Micro Teaching Cycle
- What is the time duration for the micro teaching?
- Principles of Micro Teaching
- Advantages of Micro Teaching
- Disadvantages of Micro Teaching
- Phases of Microteaching
- How to Make a Micro Teaching Lesson Plan?
- Micro Teaching Skills Lesson Plan Format
- Special Instructions and Steps of making Micro Teaching Lesson Plan for Different Skills
- Micro Teaching Skills
- What is the Difference Between Micro and Macro Teaching?
- Micro Teaching Examples
- Micro Teaching PDF and PPT Notes Download Free
What is Micro Teaching And Microteaching Skills? | Micro Teaching | Micro Teaching Skills | MicroTeaching
Concept and Introduction to Micro Teaching?
Micro Teaching is a teacher training technique that helps trainee teachers to master their teaching skills. It requires the teacher trainee:
- To use specific teaching skills
- To teach a single concept
- To teach for a short time
- To teach very small number of students
So, In this way, the teacher-trainee practices the teaching skills in terms of definable, observable, measurable, and controlled form with repeated cycles till he/she attains mastery in the use of skills.

Meaning of Micro Teaching
Micro Teaching is a procedure in which a student-teacher or trainee teacher practices teaching with a reduced number of students in a reduced period of time with an emphasis on a narrow and specific teaching skill.Definition of Micro Teaching
There are many definitions of microteaching given by scholars. Some of the micro-teaching definitions are:
D.W Allen (1996): According to D.W Allen"Microteachingis a scaled-down teaching encounter in class size and time".
R.N bush (1968):"Micro Teaching is a teacher education technique which allows the teachers to apply clearly defined teaching skills to carefully prepared lessons in a planned series of five to ten minutes to encounter with real students, often with an opportunity to observe the result on Video Tape."
L.C Singh(1977): Microteaching is a scaled-down teaching encounter in which a teacher, a small unit to a group of 5 students for a small period of 5 to 20 minutes. Such a situation offers a helpful setting for an experienced or unexperienced teacher to acquire new teaching skills and to refine old ones.
N.K. Jangira and Azit Singh (1982): "Microteaching is a training set for the student-teacher where complexities of the normal classroom teaching are reduced by:"
- practicing one component skill at a time.
- reducing the size of 5 to 10 pupils.
- limiting the content to a single concept.
- reducing the duration of the lesson to 5 - 10 minutes.
B.K. Passi and M.S Lalita (1976): "Microteachingis a training technique that requires student teachers to teach a single concept using specified teaching skills to a small number of students in a short duration of time".
M.C. Alleese and Unwin (1970):"The term micro-teaching is most often applied to the use of closed-circuit television to give immediate feedback to a trainee teacher's performance in a simplified environment."

What are the Objectives of Micro Teaching?
Some of the Aims and Objectives of Microteaching are:
- To enable teacher trainees to learn and assimilate new teaching skills under controlled conditions.
- The second objective is to enable teacher trainees to master a number of teaching skills.
- The last one is to enable teacher trainees to gain confidence in teaching.
Characteristics and Features of Micro Teaching
The main characteristics of microteaching are:
- It is a highly individualized training device and an experiment in the field of teacher education which has been incorporated in the practice of teaching schedule.
- The students are providing immediate feedback in terms of peer group feedback, tape recorder, or CCTV.
- Micro teaching is a student teaching skill training technique and not a teaching technique or method.
- Practice one skill at a time.
- Reducing the class size to 5 to 10 pupils or students.
- Limiting the content to a single concept.
- Microteaching is micro in the sense that it scales down the complexities of real teaching.
- Micro teaching advocates the choice and practice of one skill at a time.
Steps of Micro Teaching
The microteaching program involves the following 9 Steps:
- Step 1: Orientation
- Step 2: Discussion of Teaching Skill
- Step 3: Selection of a particular teaching skill
- Step 4: The practice of the Skill
- Step 5: Proving the feedback
- Step 6: Re-Planning
- Step 7: Re-teaching
- Step 8: Re-feedback
- Step 9: Repetition of the micro-teaching cycle
Step 1: Orientation
In this step particular skill to be practiced is explained to the teacher trainees in terms of the purpose and components of the skill with suitable examples. At the beginning the student teachers should be given the necessary theoretical background about micro teaching by having a free and fair discussion of aspects like those given below:
- Concept of micro-teaching
- significance of using microteaching
- The procedure of micro teaching
- Requirements and Strategies for Adopting micro-teaching techniques
Step 2: Discussion of Teaching Skill
In this step, the teacher trainee gives the demonstration of the skill of micro teaching in simulated conditions to the teacher trainees. In this step, the knowledge and understanding of the following aspects are to be developed.
- Analysis of teaching into component teaching skills.
- The discussion of the rationale and role of these teaching skills in teaching.
- Discussion about the component teaching behaviors comprising various teaching skills.
Step 3: Selection of a particular teaching skill
In this step, the teacher trainee plans a short lesson plan on the basis of the demonstrated skill for his or her practice. They are also provided with necessary orientation and processing material for the practice of that skill.
Step 4: The practice of the Skill
In this step, the trainee teachers teach the lesson to a small group of students. His / Her Lesson is supervised by the supervisor and peers where possible. The student-teacher may also have his lesson taped on a video or audiotape.
Step 5: Proving the feedback
On the basis of the observation of a lesson, the supervisor gives feedback to a teacher trainee. The supervisor reinforces the instances of effective use of the skill and draws the attention of the teacher trainee to the various points where he could not do well. Whenever possible the help may also be taken from various gadgets like audiotapes, videotapes, and closed-circuit televisions.
Step 6: Re-Planning
After getting the feedback given by the supervisor the teacher trainee re-plans the lesson plan in order to use the skill in a more effective manner in the second trial.
Step 7: Re-teaching
In this step, the revised lesson is taught to another comparable group of students. In this session of 6 minutes, the student-teacher re-teaches his micro lesson on the basis of his prepared plan or rearranged setting.
Step 8: Re-feedback
In this, the supervisor observes the re-teach lesson and gives re-feedback to the teacher trainee with convincing arguments and reasons.
Step 9: Repetition of the microteaching cycle
This is the last step of micro-teaching in which the"teach-re-teach" cycle may be repeated several times till an adequate mastery level is achieved by the trainee.
Micro Teaching Cycle
There are 6 steps that are generally involved in the micro-teaching cycle. These Six Steps are:
- Plan
- Teach
- Feedback
- Re-plan
- Re-teach
- Re-feedback

Note: There may be variations as per the requirement of the objective of the practice session.
1. Plan
It is the first step in the micro-teaching cycle. The plan involves the selection of the topic and related content of such a nature in which the use of components of the skill under practice may be made easily and conveniently. The topic is analyzed into different activities of the teacher and students. These activities are planned in such a logical sequence where the maximum application of the components of skill is possible.
2. Teach
Teaching involves the attempts of the teacher trainee to use the components of the skills in suitable situations of teaching-learning as per his / her planning of activities. If the situation is different and it is not as visualized as per the demand of the situation in the class. He / She should have the courage and confidence to handle the situation arising in the class effectively.
3. Feedback
The term feedback refers to giving information to the teacher trainee about his performance. The information includes the points of strength as well as weaknesses relating to his/her performance. This helps the teacher trainee to improve his / her performance in the desired direction.
4. Re-Plan
The teacher trainee replans his lesson, incorporation the points of strength and removing the points which are not skillfully handled during a teaching in the last attempt either on the same topic suiting to the teacher trainee for improvement.
5. Re-Teach
Re-Teaching involves teaching to the same group of students if the topic is changed or to a different group of students if the topic is the same. This is done to remove the boredom or monotony of the pupil. The teacher trainee teaches the class with renewed courage and confidence to perform better than the last attempt.
6. Re-Feedback
It is the most important component of micro-teaching which is used for behavior modification of teacher trainees in the desired direction in each and every skill practice.
What is the time duration for the micro teaching?
- Teaching Time Duration -6 Minutes
- Feedback Duration -6 Minutes
- Replanning -12 minutes
- Reteaching -6 minutes
- Re feedback -6 minutes
Principles of Micro Teaching
The principles that underlie the concept of microteaching are:
- Capabilities
- Intrinsic Motivation
- Goals are to be realistically set
- Goals are to be realistically set
- One element in one time
- Active Participation
- Information and Knowledge
- Immediate Feedback
- Experience in various skills
1. Capabilities
The first principle of microteaching is that the capabilities of the learner must be considered when a decision of what to teach is made. In this principle, the trainee is given the opportunity to select a lesson content in an area of his greatest competence so that he may feel at ease with the subject matter.
2. Intrinsic Motivation
The learner must be motivated, intrinsically. Intrinsic motivation in the context of micro-teaching is created through the cognitive and effective discrepancy between his ideas, self-concept as a teacher, and his real teaching.
3. Goals are to be Realistically Set
In this principle of microteaching, an attempt is made to modify only modifiable behavior which the trainee wants to change.
4. One Element in One Time
Only one element of modifiable behavior is to be worked on at a time. In pursuance of this principle, in any micro teaching session, a trainee practice one skill at a time and moves to the next only after he has achieved mastery over it.
5. Active Participation
In microteaching, active participation by the students is necessary in order to modify his behavior substantially. According to this principle, in any micro-teaching situation, a trainee teacher engages actively in practicing a skill in which he wants to be perfect.
6. Information and Knowledge
Knowledge and information about one's performance help the learner. According to this principle, in any micro teaching session, a trainee teacher is provided knowledge and information about his / her own performance by the supervisor with or without the help of audio and videotapes. The transfer of learning will become better if the learner gets feedback related to his performance.
7. Immediate Feedback
Immediate feedback informs the trainee teacher of their effective practice. So according to this principle, in any microteaching setting, a trainee teacher is provided immediate feedback regarding his performance, thereby eliminating any chance of wrong practice.
8. Experience in various skills
In micro teaching, students are provided experience in various skills over a considerable length of time.
Advantages of Micro Teaching
So now the question is why micro-teaching is Important? Here we have given some merits of microteaching which are as follow:
- Microteaching helps us in developing and mastering important teaching skills.
- It is very effective in modifying the behavior of the teacher.
- Another advantage is that it employs real teaching situations for developing skills.
- As micro-teaching is scaled-down teaching, it reduces the complexity of the teaching process.
- It helps us in getting deeper knowledge regarding the art and science of teaching.
- It is an individualized teacher training technique.
- It helps us in accomplishing specific teacher competencies.
Disadvantages of Micro Teaching
- The First Demerit of microteaching is that it is skills-oriented; contents are not emphasized.
- There is a special classroom setting required for micro-teaching.
- Only a few specific skills are covered.
- It deviates from normal classroom teaching.
- The number of opportunities for re-teaching and re-planning for a large number of trainee teachers is not possible.
- It is a time-consuming teaching technique.
- Many administrative problems arise while arranging microlessons.
Phases of Microteaching
There are three Phases of Micro-Teaching. Three phases of the micro teaching are as follows –
- Phase I: information Acquisition part (Pre-active phase)
- Phase II: talent Acquisition part (Interactive phase)
- Phase III: talent Transfer part (Post-active phase)
Phase I: Information Acquisition Part:
- In this part, the coed teacher tries to amass information regarding the talent, its role in the room, and its part behavior.
- He reads relevant literature.
- He also observes the demonstration lesson and also the mode of presentation of the talent.
It includes 3 vital activities:
- To produce information and awareness of specific teaching talent.
- To look at the demonstration of the teaching talent.
- To analyses and discuss the demonstration of teaching activities of the talent.
Phase II: Talent Acquisition Part:
In this part, the coed teacher prepares a small lesson, practices the talent, and carried out the microteaching cycle. Three activities area unit undertook during this phase are:
- To organize a small lesson for teaching talent.
- To apply the teaching talent in a real room scenario.
- To judge the performance.
Analysis activity provides the idea to re-plan a similar lesson for reteaching.
Phase III: Talent Transfer Part:
After exploiting mastery of the teaching talent, the teacher-trainees area unit was given the opportunity to use the talent within the traditional room scenario rather than a synthetic classroom scenario.
How to Make a Micro Teaching Lesson Plan?
The format and Template of Microteaching skills for School teachers, B.Ed, DELED, BTC, BSTC, etc. are given below.
This is the sample format of the micro-teaching lesson plan. Some Elements and Components can be added or removed according to the need. For different microteaching skills, you just have to fill and change the tally components.

Micro Teaching Skills Lesson Plan Format
Observation Schedule Cum Rating Scale Microteaching Lesson Plan Format and Template
|
Name of the Trainee Teacher: Subject: Concept/Topic: Session: Supervisor: |
Date: Roll No: Class: Duration: |
|
Trainee Teacher’s Activity |
Students’ Activity |
|
Tallies Showing the occurrence of component behavior |
|
|
Components |
Rating Scale |
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
- Micro Lesson Plan Examples
- Micro/Macro and Real Teaching Lesson Plans for B.Ed, D.EL.ED, BSTC and School Teachers
Special Instructions and Steps of making Micro Teaching Lesson Plan for Different Skills
- The Micro teaching Observation schedule cum rating scale comprises three columns.
- The first column indicates the tallies against different components of the skill.
- The second column specifies the components of the skill.
- The third column contains a rating from 0 to 6 against each of the components.
- Judgment has to be given on a seven-point scale for various aspects of the skill.
- Indicate the extent of acquisition of the various aspect of the skill by encircling (0) the appropriate number you deem fit.
- The Points of the Scale indicate the following:
- 0 - Extremely poor
- 1 - Very Poor
- 2 - Poor
- 3 - Average
- 4 - Good
- 5 - Very Good
- 6 - Excellent
Micro Teaching Skills
There are a number of microteaching skills. Major types of Micro teaching skills are:
- Skill of Introducing a Lesson
- Skill of Probing Questions
- Skill of Explanation
- Skill of Stimulus Variation
- Skill of Reinforcement
- Skill of Illustration with Examples
- Skill of Blackboard writing
- Skill of Achieving closure
- Skill of Demonstration
- Skill Of Writing Instructional Objectives In Behavioural Terms
Micro Teaching Skill of Introduction
A good introduction to the lesson is a skill, an art, which will engage students, tell them what to expect from the lesson, and provide a framework with each student can work. During the course of introducing, the teacher must not forget that the introduction of the lesson to the students is a good way to b sure that students understand what the lesson will be about.
The Skill of Introducing a lesson involves the maximum use of the previous knowledge of the students, using the appropriate device while introducing a lesson, avoiding discontinuity, and avoiding irrelevant statements.
The major Components or Elements of Introduction Skill of Microteaching are:
- Maximum Utilization of Previous knowledge of the students.
- Using Appropriate Device
- Maintenance of continuity.
- Relevancy of verbal or non-verbal behavior.
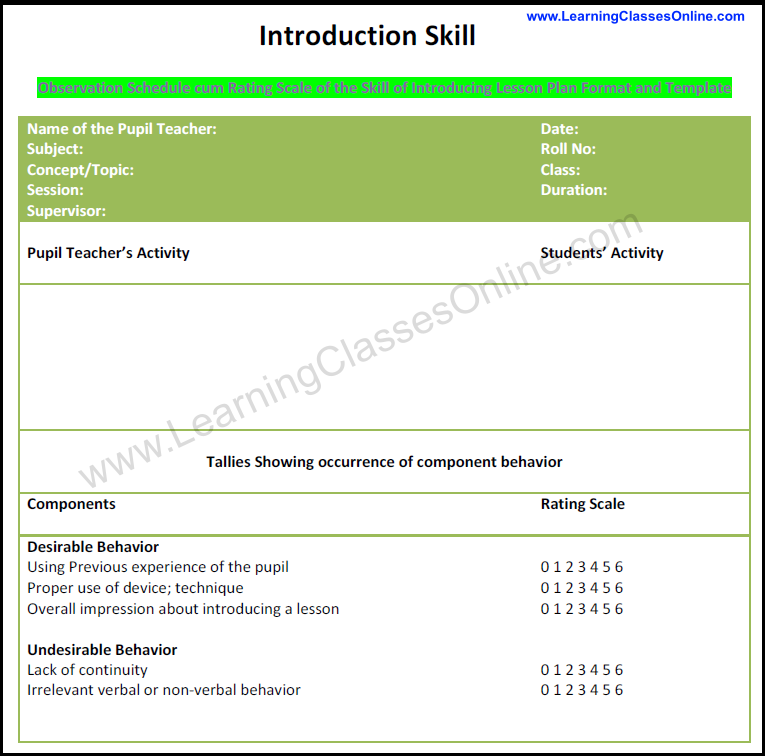
Skill of Introducing Lesson Plan Format
|
Name of the Trainee Teacher: Subject: Concept/Topic: Session: Supervisor: |
Date: Roll No: Class: Duration: |
|
Trainee Teacher’s Activity |
Students’ Activity |
|
Tallies Showing occurrence of component behavior |
|
|
Components |
Rating Scale |
|
Desirable Behavior Using Previous experience of the pupil Proper use of the device; technique The overall impression of introducing a lesson Undesirable Behavior Lack of continuity Irrelevant verbal or non-verbal behavior |
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
- Lesson Plan Examples for Skill of Introducing a Lesson
- Sample Lesson Plans on Microteaching Skill of Introducing Lesson for B.Ed, DE.L.Ed,BTC and School Teachers
MicroTeaching Skill of Questioning
The success of teaching or art with which we put questions very must depend upon the micro-teaching skill of questioning, so the while fabric of the classroom teaching-learning process is being weaved around the activities associated with the use of questioning skills on the part of teaching.
According to Parker"Questioning is the key to all educative activity."
Thring's View: "Teaching means skillful questioning to force the mind to see, to arrange, to act."
So in Simple words, questioning skill can be defined as a teaching skill that is helpful in putting the desired, meaningful, clear, relevant, precise, specific, grammatically correct, simple, and straightforward questions to the students in a classroom teaching-learning situation for the purpose of testing their knowledge and understanding.
What is The Purpose and Functions of Questioning Skill of Micro Teaching?
Prof. Frank A. Butter emphasizes the following purpose of questions.
- To Change Viewpoints
- To bring out cause and effect
- To develop new ideas
- To promote understanding
- To develop an appreciation
- To create a mindset
- To test the objective thoughts
- To apply information
What are the Types of Questions that should be asked in the teaching-learning process to make it more effective?
- Natural Questions
- Formal Questions
- Introductory or Preliminary Questions
- Re-capitulatory Questions
- Higher-Order Questions
How to Ask Questions?
- Address questions to the whole class.
- Distribute questions to the whole class.
- Allow sufficient time to think
- Do not repeat questions
- Occasionally ask questions to back-benchers.
- Aks questions in such a manner as not to suggest the answer
- Show adaptability in questioning
- Audible to all.
- Be cheerful and jovial
- Avoid elliptical as well as echo and double-barrelled questions
----> The teacher must be sure that he/she may have a clear purpose for their question rather than just determining what knowledge is known. This type of question planning results in designing questions that can expand students the knowledge and encourage them to think creatively.
- Skill of Questioning Examples
- Sample Lesson Plans on Microteaching Skill of Questioning Lesson for B.Ed, DE.L.Ed, BTC and School Teachers
Micro Teaching Skill of Illustration With Examples
The micro-teaching skill of Illustration for example provides a sense of authority to the teacher. At a given time, when the teacher inspires that the student in the classroom grasps the content of the lesson quickly, the skill requires that the teacher uses a personal and specific example to illustrate the content of the topic.
Illustrate the subject matter with the help of an example is necessary to clarify, verify, or substantiate the concept. Proper use of this teaching skill can enrich the communication skill of the teacher as well as that of the student and make the study memorable.
Significance and Importance of Illustration Skill
- With the help of this skill, the teacher becomes enabled to command and to have the attention of the pupils with remarkable effectiveness.
- Besides, this skill can stir up emotion and thus may reach the conscience and the heart of the student. The skill; is also an effective memory aid and thus it must be used by every teacher for result-oriented teaching.
- Illustration combined with example usually requires only a few words, yet they can paint vivid mental images and if chosen carefully and used skillfully they can prove out to be very fruitful. However, a teacher may reinforce their value by adding a brief explanation.
- This specific skill may include numerous illustrations and examples drawn from practical experience by the teacher which can be used in the teaching.
- The Illustration with Example Skill of Micro Teaching is so essential in the context of the topic that sometimes the illustration themselves can explain the content of the topic concerned.
- Illustration along with the example, if they are quite accurate and appropriate to the content of the topic concerned as well as pleasing to the eyes, then they would serve the purpose of the teacher in a rewarding manner.
- The picture must support the text. The fewer the number of words, the more the illustration must convey.
- Understanding how illustration shows visual elements such as line, color, shape, texture, and composition can help to appreciate and understand the artist; intention through the artwork. The student would also be to identify illustration; styles such as realistic, impressionistic, expressionistic, abstract, primitive, and surrealistic.
- Early exposure to the illustration along with related examples helps to develop aesthetic sensitivities amongst the students.
General Guidelines for the Effective Use of the Micro Skill of Illustrations
The following guidelines may be used by the teacher for effectively using the skill of illustration for example in micro-teaching.
- Start with the simplest Example
- Illustration and Example within a comprehensive level of student
- Non-Relevant Illustration and Example Also
- Limited Number of Illustrations
- The illustration is for Clarification of an idea
- Asking the students to provide some more example
1. Start with the simplest Example:
The teacher should start teaching with the use of simple illustration along with the example and move on to the complex ones in an ascending manner. A basic principle of concept formation is that an example given to illustrate a concept confronts the learner with a complex sorting task.
Some of the information conveyed by the illustration / Example may be quite relevant whereas it may be somewhat irrelevant also. If the teacher being with complex illustrations, the student may become confused by excess information and miss the point. Therefore, the teacher must be with a simple example and work up to complex ones, emphasizing only the relevant aspect of the subject matter.
2. Illustration and Example within a comprehensive level of student:
If the illustration and the example are not within the range of the student's experience and knowledge i.e. within their comprehensive level, then they are useless as an illustration of the concept. But the question arises as to how to know that an illustration or an example is appropriate for the students.
This information is a function of the teacher's familiarity with the student's background. The more a teacher knows about the students, the more the teacher would be able to select relevant illustrations and examples.
3. Non-Relevant Illustration and Example Also:
After presenting some illustration and example, the teacher should use one irrelevant or not so relevant illustration along with the example in order to sharpen the student's understanding. That would mean once the student has acquired a basic understanding of the concept, then the use of one such irrelevant or not so relevant to the concept illustration/example would help the student to discriminate between the concept actually being taught than that of some other concept.
However, care should be taken not to include irrelevant illustrations or examples too early in the presentation; otherwise, the student may get confused unless they have fully grasped the content of the topic concerned.
4. Limited Number of Illustrations:
The teacher should keep into consideration that giving a number of illustrations would not prived the student with a better chance of comprehending the contents. Therefore, unless the additional example illustrates a new aspect of the concept, or provides more information about it, they are not going to add anything extra to the students' understanding; rather they may confuse the students.
5. The illustration is for Clarification of an idea:
The teacher must always take into consideration that the actual purpose of using an example is to illustrate, clarify, or substantiate an idea. Therefore the teacher must relate the example to the idea should not assume that the student would automatically connect the example they are given with an idea.
6. Asking the students to provide some more example:
There is one way through the use of which the class teacher and the aid way is to ask the student to provide some additional examples pertaining to the subject taught. If their example is good, then that ensures that the student has grasped the concept properly. If their example is faulty, they have probably misunderstood, and then the teacher can pinpoint their misconception about the lesson.
How can the Microteaching Skill of Illustration prove out to be fruitful for the class teacher in the classroom?
The specific skill of illustrating with an example can prove out to be fruitful for the class teacher in the following ways:
- Attracting Attention
- Aiding Retention
- Aiding Retention
- Boosting Comprehension
- Creating Context
1. Attracting Attention: Showing a photograph of a dramatically beautiful rainbow at the opening of a presentation on the topic of light proves out more helpful in attracting the attention of the student than explaining the contents.
2. Aiding Retention: Providing a chart showing the color of VIBGYOR organized according to the color classification would naturally prove out to be fruitful to the teacher and might be viewed as primarily aiding retention.
3. Boosting Comprehension: Drawing a diagram illustrating the seven colors of the rainbow in their natural order will naturally help the teachers in explaining the process for boosting up the comprehension level of the students.
4. Creating Context: When the student is given the opportunity to visualize the photograph, chart of VIBGYOR, diagram of seven colors, and draw their own conclusion in terms of their understanding, which may lead to the creation of the context.
Conclusion: In a nutshell, it can be said that the appropriate use of the micro teaching skill of illustration for example is such a fruitful teaching aid that can enrich the communication skills of the teacher, touch the heart of the student, and make the topic taught quite memorable. On the other hand, if this skill or methodology is handled improperly. it may divert the attention of the student from the valuable instruction. Nonetheless, it is quite a useful, helpful, and rich dividend-paying skill.
- Illustration Skill Examples
- Sample Lesson Plans on Microteaching Skill of illustration with the example for B.Ed, DE.L.Ed, BTC and School Teachers
Micro Teaching Skill of Explanation
We have been using explanation as an intellectual activity. Concepts, ideas, or phenomena are communicated to make them understandable to others by giving examples showing relationships, etc. Explaining is an activity which shows the relationship among various concept, ideas, event, or phenomenon.
The attempt is made to relate a set of facts with another set of facts to promote understanding. A teacher has to learn the skill of explaining in order to make the students understand clearly many ideas, concepts, and principles that need explanation. A teacher who can explain things well will go a long way in making his lesson effective.
Meaning of Explanation in Behavioural Terms:
A teacher is said to be explaining when he is describing how, why, and sometimes what of a concept, principle, phenomenon, event, action, or condition.
The micro teaching skill of explaining is defined as an act of bringing about an understanding in someone about a concept, a principle, or a phenomenon.
It has been regarded as a set of interrelated statements made by the teacher in order to increase the understanding of the students about ideas, concepts, and phenomena. While explaining, cause for the phenomenon; the reason behind the action and various logical steps involved in arriving at inferences are given in interrelated selected logical steps involved in arriving at inferences are given in the interrelated selected statement.
The Two Main Aspects of Explanaing Are:- Selection of Appropriate Statement
- Interrelating and Using the Selected Statements
1. Selection of Appropriate Statement: According to the level of the students i.e age, maturity, previous knowledge, and content of the concept, principle, or phenomenon.
2. Interrelating and Using the Selected Statements: For the proper understanding of the concept, principle, or phenomenon.
Generally, there are 3 types of statements:
- Descriptive Statements
- Interpretive Statement
- Reason giving Statements
A good explanation is one that is understood by the students. To make an explanation effective, the teacher has to increase the occurrence of desirable behavior and avoid the use of undesirable behavior.
Components of Explanation Skill of MicroTeaching
Explanation skill has12 Behavioural components which can be divided into desirable and undesirable categories.
A. Desirable Behaviour- Explaining Links
- Introductory Statement
- Concluding Statement
- Use of VIsual TEchniwque
- Technical Words defined
- Interesting of Students
- Covering Essential points
- Testing students understanding
B. Undesirable Behaviour
- Irrelevant Statement
- Lacking continuity in Statement
- Lacking in frequency
- Vague words or phrases
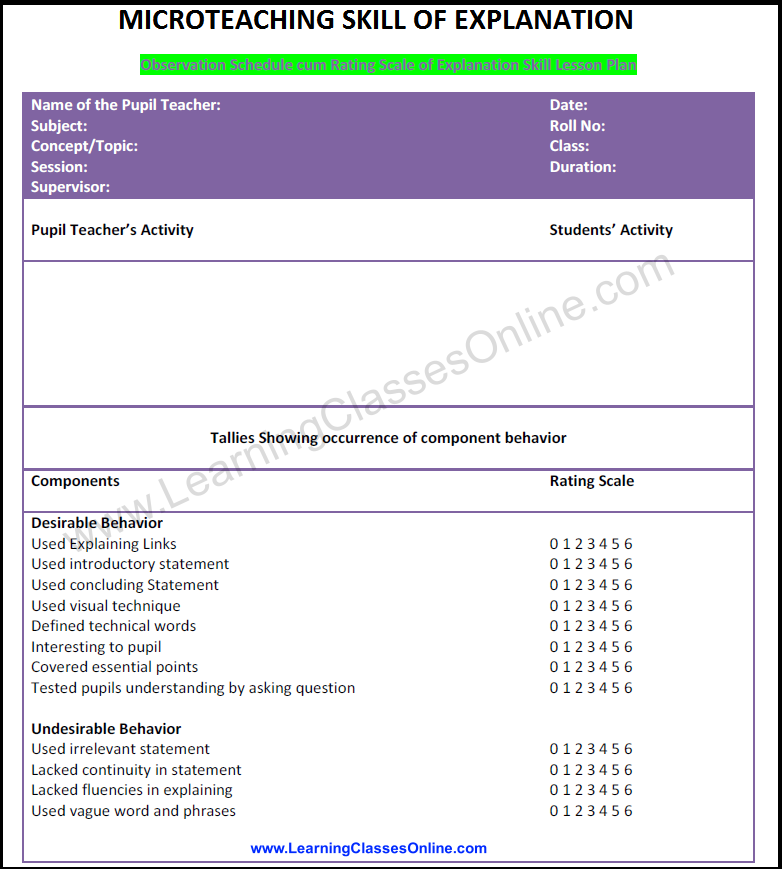
Micro Teaching Explanation Skill Lesson Plan Format
Observation Schedule cum Rating Scale Of Micro Teaching Explanation Skill Lesson Plan Format
|
Name of the Trainee Teacher: Subject: Concept/Topic: Session: Supervisor: |
Date: Roll No: Class: Duration: |
|
Trainee Teacher’s Activity |
Students’ Activity |
|
Tallies Showing occurrence of component behavior |
|
|
Components |
Rating Scale |
|
Desirable Behavior Used Explaining Links Used introductory statement Used concluding Statement Used visual technique Defined technical words Interesting to pupil Covered essential points Tested pupils understanding by asking the question Undesirable Behavior Used irrelevant statement Lacked continuity in statement Lacked fluencies in explaining Used vague word and phrases |
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
- Lesson Plan Examples for Skill of Explanation in Micro Teaching
- Sample Lesson Plans on Microteaching Skill of Explaining for BEd, DE.L.Ed, BTC, BSTC, and School Teachers
-----> It can be said that the explanation skill means as a set of interrelated statements made by the teacher related to a phenomenon an idea etc. in order to bring about or increase understanding among the student about the same presentation of the subject matter in the simplified form before the student and making it acquirable is called micro-teaching skill of Explanation.
How will you make the Explanation Effective?
Well by keeping in mind the following points mentioned below, you can make your explanation skill more effective.
- Clear Aim
- Logical Sequence
- Adequate Speed
- Simple language
- Use of Blackboard
- Use of Illustrative aids
- Use of Questions
- Use of Summary
- Proper Time
- Level of Students
- Avoiding irrelevant things
Micro Teaching Skill of Stimulus Variation
Microteaching Skill of Stimulus Variation can be defined as the change in teacher behavior to attract the pupil's attention. To catch the attention of the students, the teacher uses various stimuli in the classroom so that they may produce maximum responses.
Definition of Stimulus Variation Skill
According to Sneha Joshi, "What to change, when to change, and how to change requires skill on the part of the teacher for securing and sustaining attention at a high level. Such a skill is named as the skill of stimulus Variation."
Components of Stimulus Variation Skill
- Movement
- Gesture
- Change in Speech Pattern
- Focusing
- Change in Interaction Style
- Oral Visual Switching
- Pausing
- Physical involvement of the student

Stimulus Variation Skill of MicroTeaching Lesson Plan Format
Observation Schedule cum Rating Scale of Stimulus Variation Skill of MicroTeaching Lesson Plan Format
|
Name of the Trainee Teacher: Subject: Concept/Topic: Session: Supervisor: |
Date: Roll No: Class: Duration: |
|
Trainee Teacher’s Activity |
Students’ Activity |
|
Tallies Showing occurrence of component behavior |
|
|
Components |
Rating Scale |
|
Movement Gesture Change in Speech Pattern Focusing Change in Interaction style Oral visual switching Pausing Physical involvement of the pupils |
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
- Lesson Plan Examples for Stimulus Variation Skill
- Sample Lesson Plans on Microteaching Skill of Stimulus Variations for B Ed, DEd, BTC, and School Teachers
Concluding Remarks: Now, it is hoped that you have understood the importance and meaning of all the micro-teaching skills, examples, exercises, and observation schedules that have been provided. This should help you to prepare your micro lesson for practice teaching and gain competence in the use of the skill of stimulus variation.
What is the Difference Between Micro and Macro Teaching?
The major difference in micro and macro teaching lesson plans is the duration of time the teacher teaches in the classroom.
Generally, in Microteaching the time duration is 6 minutes and in macro teaching, the duration will be 30 minutes.
Micro Teaching Examples
In teacher training programs like B.Ed, D.EL.ED, BTC, BSTC, etc., the trainee teacher has to make micro-teaching lesson Plans of different skills for demo teaching.
If you are confused with How to make Microteaching Lesson Plans for different Subjects. Then not to worry Here we have given thousands of Microteachingsample lesson Plan examples for the subjects like English, Mathematics, Science, Social Science, Computer, Economics, Commerce and so on for all the skills with the help of which you can make your micro lesson plan easily and quickly.
Not only micro but also macro and real teaching lesson plan examples are provided in the links given below. Just Simply click on the links you will get so many micro lesson plan examples of the skill of introducing the lesson, the skill of reinforcement, the skill of questioning, the skill of stimulus variation, the skill of explanation.
Sample Micro, Mega, and Real Teaching Lesson Plan Examples of
- English
- Math
- Science
- Social Science
- Home Science
- Biological Science
- Computer
- Commerce
- Economics
- Hindi
- Sanskrit
- Other Subjects
- All Subjects
Sample Micro Teaching B.Ed Lesson Plans For Maths (All Skills)
|
S. No. |
Name Of The Skill |
Link |
|
1 |
Writing Instructional Objectives In Behavioral Terms Lesson Plan |
Click |
|
2 |
Introducing A Lesson |
Click |
|
3 |
Blackboard Writing Skill Lesson Plan |
Click |
|
4 |
Fluency In Questioning Micro Lesson Plan |
Click |
|
5 |
Probing Questioning Lesson Plan |
Click |
|
6 |
Stimulus Variation Skill Lesson Plan for Micro Teaching |
Click |
|
7 |
Explaining Skill Lesson Plan |
Click |
|
8 |
Demonstration Skill Lesson Plan |
Click |
|
9 |
Reinforcement Skill Of Microteaching Lesson Plan |
Click |
|
10 |
Achieving Closure Skill Lesson Plan |
Click |
Sample Micro Teaching B.Ed Lesson Plan For Science
|
S. No. |
Name Of The Skill |
Link |
|
1 |
Writing Instructional Objectives In Behavioural Terms |
Click |
|
2 |
Introduction Skill |
Click |
|
3 |
Blackboard Writing Skill |
Click |
|
4 |
Fluency In Questioning |
Click |
|
5 |
Probing Question Skill |
Click |
|
6 |
Stimulus Variation |
Click |
|
7 |
Explanation Skill |
Click |
|
8 |
Demonstration Skill |
Click |
|
9 |
Reinforcement Skill |
Click |
|
10 |
Skill of Achieving Closure |
Click |
Micro Teaching PDF and PPT Notes Download Free
List of the Topics Covered in the notes:
- Teaching Skills & Micro Teaching
- What Is Teaching?
- Defects In Teaching
- What Is Learning?
- How does Learning Happen?
- Changes In Teachers’ Role
- Changes In Students’ Role
- How do We learn Teaching Ability?
- Teaching Skills
- Introduction Skill
- Explanation Skill
- Probing Questions Skills
- Stimulus Variation Skill
- Skills Of Using Teaching Aids
- Skills Of Closure
- Microteaching
- Micro Teaching In India
- Micro Teaching Cycle
- Components Of Microteaching
- Phases Of Microteaching
- Microteaching Swirl
- Microteaching Vs Macro teaching
- Characteristic Of Microteaching
- Merits Of Micro Teaching
- Demerits Of Microteaching
Quick Links:
- Download Micro Teaching PPT
- Download Micro Teaching Skills Lesson Plans PDF of All Subjects
- Microteaching Skills in B.Ed
Micro Teaching Notes for B.Ed
Micro-Teaching – Detailed Notes for B.Ed.
If you are pursuing B.Ed. or D. El. Ed., you probably know about micro-teaching. It is very important to learn microteaching in your B.Ed. course. Everyone needs to practice micro-teaching. This is a post on micro teaching explaining the meaning, definitions, characteristics, steps, phases, advantages, and disadvantages of micro-teaching. Basically, this is notes on “Micro-Teaching or Microteaching” for B.Ed.
Micro-Teaching: Meaning, Characteristics, Steps, Phases Advantages, and Disadvantages
Microteaching is a significant development in the teacher education program. The basic objective of microteaching is to make teacher education programs scientific, effective, and meaningful. Microteaching was developed by professors Dwight Allen and Robert Bush
at Stanford University in 1963.
Meaning of Micro-Teaching
A scaled-down version of real teaching and several factors. Scaled-down in terms of class, size, and time in order to minimize the complexities of normal teaching. Micro-teaching is a training technique in which a teacher trainee practices with a small group of 5 to 10 pupils for a short duration of 5 to 10 minutes on a selected content/ concept in a single skill.
Micro-teaching is a stimulated social teaching process to provide feedback to teacher trainees for the modification of the behavior of teacher trainees. Micro-teaching provides teachers with a practice setting or instruction in which the normal complexities of the classroom are reduced and the teacher gets feedback on their performance.
The student teachers are required to teach a single concept using specified teaching skills to a small number of students in a short duration of time.
Definition of Micro-Teaching
DW Allen (1966) defined, “Microteaching as a scale down teaching encounter in class size and period.”
Clift (1976) defined, “Microteaching as a teacher training procedure, which reduces the teaching situation to simpler and more controlled encounter achieved by limiting the practice to a specific skill and reducing teaching time and class size.”
B.K. Passi (1976) defined, “Microteaching as a training technique, which requires student teachers to teach a single concept using specified teaching skill to a smaller number of pupils in a short duration of time.”
Allen and Eve (1968) defined, “Microteaching as a system of controlled practice that makes it possible to concentrates on specified teaching behavior and to practice teaching under controlled conditions.”
Mc. Knight (1971) defined,” Microteaching is a scaled-down teaching encounter designed to develop new skills and refine old ones.”
Flanders, Ned. A. (1970) defined, ”Microteaching program is organized to expose the trainees to an organized curriculum of miniature teaching encounters, moving from the less complex to the more complex.”
Characteristic of Microteaching
Microteaching is an Associate in Nursing’s analytical approach to coaching. Microteaching provides adequate feedback. It’s a coaching device to organize effective lecturers. Microteaching could be an extremely personalized coaching technique. The use of videotape makes observation terribly objectives. Microteaching could be a coaching technique and not a teaching technique.
Microteaching is scaled down teaching:
- (a) It reduces the category scrutinization to five to ten pupils.
- (b) It reduces the period of amount five to ten minutes.
- (c) It reduces the dimensions of the subject.
- (d) It reduces the teaching talent.
Objectives of Micro-Teaching
Objectives of micro-teaching are given below –
- To find out and assimilate new teaching skills underneath controlled conditions.
- To realize confidence in teaching and mastering a variety of teaching skills on a small size of pupils.
- To utilize the obtainable material and time to the most.
- To modify the teaching method to achieve perfection in teaching.
- To amass mastery during a range of teaching skills.
- To switch the teaching behaviors within the needed manner.
- To scale back the complexities of teaching.
- To amass new teaching skills and refine previous ones.
- To produce needed feedback.
Another objective of micro-teaching is that Micro-teaching aims at providing part skills of the teacher to the teacher trainees at the pre-service level.
Steps of Microteaching
In microteaching, the trainer should follow the following steps in a systematic manner to achieve the required skills among the trainees.
Orientation program with the student-teacher: The teacher education should provide and enlighten about micro-teaching and its importance in the teaching-learning process to develop teaching efficiency.
Discussing teaching skills: The teacher educator should discuss the definition of the skill and identify different skills, which affect the teacher’s behavior.
Selection of a particular skill: Among the different skills, the teacher educator should select a suitable and particular skill, which is required for the topic in the concerned subject.
Presenting a model demonstration lesson on a particular skill: The teacher educator should demonstrate in a micro lesson in a particular skill, which is selected for demonstration.
Observation of the model skill by student teachers and recording their observations on the observation schedule: The student teachers should observe the model micro lesson performed by the teacher educator.
Critical appreciation of the model lesson by student teachers: The student teachers should discuss the model micro lesson with the teacher educator in detail and achieve the required skill.
Creation of a microteaching setting: The Indian model of micro-teaching developed by NCERT gives the following settings.
- The number of students is about 5 to 10.
- The duration of the time is about 5 to 10 minutes.
- Number of skills only one.
- Duration of the microteaching cycle: 36 minutes.
- Observers: peers and teacher educators.
Practicing the skill: The student teachers should practice a particular skill to the satisfaction of the observers.
Providing feedback: The performed micro lesson should be followed by the feedback for knowing not only the mistakes but also modifications in that lesson.
Re-planning: After the feedback on the performed micro lesson, the student-teacher should re-plan the same or different micro lesson by including the suggestions of the observers.
Re-teaching: Re-planed micro lessons should be taught to the same or other groups of students consisting of five to ten students.
Providing re-feedback: Feedback is given again in the re-teaching of a micro lesson as re-feedback. The practice should be continued until the observers are satisfied with the skill achieved.
Integration of teaching skills: Finally the student teachers should integrate
the acquired skills and perform a lesson as link practice.
Advantages of Micro-Teaching
The Advantages of micro-teaching are given below.
- It reduces traditional schoolroom teaching by scaled-down teaching.
- Its objectives square measure well outlined.
- Micro-teaching is helpful for developing teaching potency in pre-service and in-service teacher education programs.
- Micro-teaching is a good feedback device for the modification of teacher behavior.
- The information and application of teaching skills are given by the utilization of microteaching.
- It provides for self-analysis through the magnetic recorder and videotape.
- Microteaching could be a coaching device for rising teaching apply and prepares effective academics.
- Micro-teaching is coaching for real teaching.
- It minimizes the complexities of traditional schoolroom teaching.
- Micro-teaching facilitates in increase confidence step by step.
- Because it is an Associate in Nursing personal coaching device, every initiate makes progress at his own rate reckoning on his ability.
- It’s simply noticeable, measurable, achievable, modifiable, and practicable.
Disadvantages of Micro-Teaching
The disadvantages of micro-teaching are given below.
- Microteaching is an incredibly time intense technique.
- Microteaching is ability orientated instead of content orientated.
- Scope of microteaching is slim.
- Non-convenience of a microteaching laboratory.
- A sizable amount of trainees can not be given chance for re-teaching and replanning.
- Microteaching is carried with success solely during a controlled environmental state of affairs.
- The fortunate implementation of microteaching needs competent and suitably trained academics.
- Microteaching doesn’t take into thought the general setting of teaching.
- It doesn’t offer broad, primarily based behaviors in terms of skills.
- It wants sufficient time to impart the teaching skills among all the coed teachers.
- It needs video, magnetic recorder, and different devices for creating the small lesson terribly effective. It becomes tough for coaching schools to create such arrangements.
Major Skills of Microteaching practiced in Teacher Training Institutions
- Skill of writing instructional objectives in behavioural terms
- Skill of Introducing a Lesson
- Skill of Black board Writing
- Skill of Fluency in Questioning
- Skill of Probing Questioning
- Skill of Stimulus Variation
- Skill of Explaining
- Skill of demonstration
- Skill of reinforcement
- Skill of achieving closure
Tags:
micro teaching
micro teaching skills
skills of micro teaching
skills in micro teaching
skill of micro teaching
what micro teaching
micro teaching hindi
what is micro teaching
micro teaching in hindi
definition of micro teaching
micro teaching ppt
micro teaching pdf
components of micro teaching
principles of micro teaching
micro teaching cycle
steps of micro teaching
concept of micro teaching
types of micro teaching
micro teaching definition
micro teaching lesson plan
micro teaching skills pdf
micro teaching skills illustrating with examples
advantages of micro teaching
characteristics of micro teaching
importance of micro teaching
define micro teaching
disadvantages of micro teaching
objectives of micro teaching
microteaching
skills of microteaching
microteaching definition
microteaching cycle
steps of microteaching
microteaching ppt
microteaching lesson plans
microteaching lesson plan
phases of microteaching
microteaching pdf
microteaching presentation
phases of microteaching pdf
skill of questioning in microteaching
importance of microteaching
define microteaching
advantages of microteaching
introduction skill in microteaching
introduction skill in microteaching ppt
List of Topics Covered:
Micro Teaching: Concept and Introduction
Meaning and Definition of Micro Teaching
Objectives and Characteristics of Micro Teaching
Steps of Micro Teaching
Micro Teaching Cycle
Principles of Micro Teaching
Advantages and Disadvantages of Micro Teaching
How to Make a Micro Lesson Plan?
Micro Teaching Skills
All Types of Micro Teaching Skills in Details with Format and Lesson Plan Examples
Skill of Introducing a lesson
Skill of Probing Questions
Skill of Illustration with Examples
Skill of Explanation
Skill of Stimulus Variation
Skill of Reinforcement
Micro Vs Macro Teaching
Microteaching Lesson Plans
Micro Teaching Downloadable PPT and PDF Notes
Similar Posts
💁Hello Friends, If You Want To Contribute To Help Other Students To Find All The Stuff At A Single Place, So Feel Free To Send Us Your Notes, Assignments, Study Material, Files, Lesson Plan, Paper, PDF Or PPT Etc. - 👉 Upload Here
अगर आप हमारे पाठकों और अन्य छात्रों की मदद करना चाहते हैं। तो बेझिझक अपने नोट्स, असाइनमेंट, अध्ययन सामग्री, फाइलें, पाठ योजना, पेपर, पीडीएफ या पीपीटी आदि हमें भेज सकते है| -👉Share Now
If You Like This Article, Then Please Share It With Your Friends Also.
Bcoz Sharing Is Caring😃


Very good. Thanks
ReplyDeleteVery very good and helpful
ReplyDeleteVery nice work
ReplyDeletePost a Comment
Please Share your views and suggestions in the comment box