ICT File | Critical Understanding of ICT in Education B.Ed First and Second Year Practical File in English Medium Free Download PDF | ICT Notes, Files, Assignment, Project and Text Book in English
Hello Friends, Welcome To Our Website www.Learningclassesonline.Com. If You Are Looking For Critical Understanding Of ICT Practical File In English For B.Ed Or Any Other Course. So You Are In The Right Place.
Here You Will Get Free Notes And Sample Practical Files To Prepare The ICT File. The Button To Download The Critical Understanding Of ICT File In English PDF Is Given Below The ICT Notes.
Just Click On The Button And Download The ICT File.
We Have Also Provided Some ICT Notes Below. You Can Make Your ICT And Computer Practical File, Project And Assignment Very Easily With The Help Of These Ict Notes.
- ICT Notes in English
- Introduction To Computer
- Characteristics Of Computer
- Classification Of Computer
- Microcomputers
- Minicomputers
- Mainframes
- Super Computers
- Components Of A Computer System
- Computer Devices
- Input Devices
- Output Unit
- Memory Unit
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Microsoft Excel
- Internet
- Application Of Internet
- Hardware And Software Requirements For Internet
- Surfing Internet
- Web Browser
- Web Search Engine
- Handling Available Equipment
- Epidiascope
- Overhead Projector
- Tape Recorder
- Television
- Video Cassette Recorder
- Slide Projector
- Smart Classroom
- Critical Understanding of ICT B.Ed Practical File in English Download PDF
- Check Latest ICT Files and Help Books Online
- Buy ICT Study Material Online at Lowest Price
ICT And Computer Short Notes In English - (Critical Understanding of ICT - Information And Communication Technology) ICT Practical File Notes PDF For B.Ed 1st and 2nd Year in English Medium
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER
The word “COMPUTER” originates from the word “COMPUTE” which means to calculate. The earlier computer was considered to be a calculating device, which can perform arithmetic operations at enormous speed.
It is a data processing device, i.e. it is an automatic electronic machine or device which accepts raw information as an input and reveals useful information as output or its processes according to a list of instructions and gives the output.
It can perform a variety of jobs which are mentioned as under:
- Speedy and accurate calculations
- Storage of information
- Retrieval of information
- Combining information
- Sorting information
- Processing of information
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTER
The following are the characteristics which computers possess:
1. Speed:
A computer is a very fast device. It can perform in few seconds, the amount of work that a human being can do in an entire year. The speed of a computer measure in microseconds(10-6), nanoseconds(10-9), and picoseconds (10-12). A powerful computer is capable of performing several billion arithmetic operations per second.
2. Accuracy:
The computer is a very accurate device. The accuracy of a computer is principle high. The degree of accuracy of a particular computer depends upon its design.
3. Automatic:
A machine is no sooner than done to be automatic if it, works by itself without human intervention. A computer is an automatic machine because one started on a job, they carry on, until the job is finished, without any human assistance. However, computers being machines can not start themselves. They cannot go out find their own problems and solutions. They have to be instructed.
4. Diligence:
The computer has, unlike human beings. A computer is free from dullness and lack of concentration. It can continuously work for hours without creating any error. The computer can perform a number of calculations with exactly the same accuracy and speed as the first one.
5. Versatility:
Versatility is the most important characteristic of the computer. It means the capacity to perform completely different types of work. You may use your computer to prepare payroll slips. Next moment you may use it for inventory management or to prepare electric bills. A computer is capable of performing almost any task if the task can be reduced to series of logical steps.
6. Memory:
The computer has a brain but unlike human beings. A computer can store data and information And recall it as long as you require it, for any numbers of years. Because of its secondary storage capability. Data and information can be retrieved as long as desired by the user and can be recalled when required. The information recalled would be as accurate as on the day when it was fed to the computer.
7. I.Q.(Intelligence Quotient):
A computer is not a magical device. It is no intelligence of its own. Users can determine, what tasks will the computer perform. So a computer cannot take its own decision as you can.
8. No Feelings:
The computer has no feelings. They have no emotions because they are machines. The computer is not like the human heart and soul. The computer cannot make such judgments on its own. Their judgment is based on the instructions given to them in the form of programs, that are written by us.
Classification of Computer
Modern computers are electronic and digital. These digital computers are broadly classified into the following four categories depending upon their performance, size, and cost.
- Microcomputers
- Minicomputers
- Mainframes
- Super Computers
1. Microcomputers :
These are low-cost small-size computers. These have been named microcomputers on account of their employing microprocessor. They represent a typically single-user system, meaning that a microcomputer can be used by only one user at a time. The personal computers (PC) that you are using in your computer lab are microcomputers. These are named personal because they can be used by any person for personal use.
2. Minicomputers:
Minicomputers perform better, are larger in size, and cost more than microcomputers. They also possess larger storage capacities and are faster in speed. Normally, they are designed to support more than one user at a time. That is why these may also be used as servers in LAN. Minicomputers, thus a multiuser computer, can support ten to hundreds of users simultaneously.
3. Mainframes:
Mainframe computers are more powerful and faster than minicomputers. They have a quite larger storage capacity and are able to support many hundreds of users simultaneously. Their real value lies in their processing power to handle large database systems i.e. handling the records of thousands of employees working in an organization.
4. Super Computers:
Where microcomputers lie at the lowest end of the computer range, the supercomputers stand at the highest end of the computer range. They are the most powerful, fastest, and most expensive machines and thus can be afforded only by the rare organization working on the national level. These computers have remarkable performance as billions of calculations may be performed by them in a second. Some of the areas in which supercomputers are being used may be mentioned as
- sophisticated scientific and biomedical researches,
- weather forecasting,
- designing of the sophisticated machines and
- warfare equipment etc.
Components of a Computer System
All general-purpose computers require the following hardware components:
- Memory:- Memory Enables a computer to store at least temporarily data and programs.
- The central processing unit (CPU):- The heart of the computer, is the component that actually executes instructions.
- Mass Storage:- It Allows a computer to permanently retain large amounts of data. Common mass storage devices include disk drives and tape drives.
- Input Unit:- Usually a keyboard and mouse the input device is the conduit through which data and instructions enter a computer.
- Output Unit:- A display screen, printer, or another device that lets you see what the computer has accomplished.
Computer Devices:
1. Input Devices:
Input devices are those devices that are meant for feeding data and instructions into the memory of the computer in computer understandable form. Some input devices are given below:
- Keyboard: A computer keyboard is one of the primary input devices for a computer system. Many styles of keyboards exist, but a few common components of most keyboards include a keypad, a QWERTY-style keyboard, and function buttons. Keyboards may also contain special knobs and buttons at the top for opening Internet browsers and other applications in addition to controlling volume.
- Mouse: Mouse is another wide input device. It is a pointing device that is used in the process of feeding the data. It is moved across a flat surface or a plane table. It is supported by a long wire which is connected to the motherboard of the computer. It shows the arrow-like image on the screen. This arrow is called a mouse pointer.
- The mouse is associated with two or three push buttons that can be gently pressed by the fingers.
- When the mouse is activated, we see a flashing arrow on the monitor screen.
- When the mouse is moved on the surface of the table or mouse pad, this arrow comes in the movement.
2. Output Unit:
In the world of computers, input/output (I/O) refers to the communication between a computer and the user. Input is the data sent to the system, whereas the output is the data sent by the system to the outside world.
Computer output devices are computer hardware equipment, that is used to communicate the results of data processing carried out by a computer to the user.There are a number of devices, which produce data in different forms, which include audio, video, or hard copy.
The output devices of computers are types of peripheral hardware connected, that is connected to the computer, either using cables or over a wireless network. Immaterial whether you have desktop computers, laptop computers, supercomputers, etc., you will require at least one computer output device.
Types of Output:
Monitor:
A monitor is also called a video display terminal (VDT). The visual display of the processed data, which the users can view is got through the monitor. Computer monitors come in a variety of screen sizes and not to forget visual resolutions. There are two types of computer monitors available, namely CRT and flat panel.
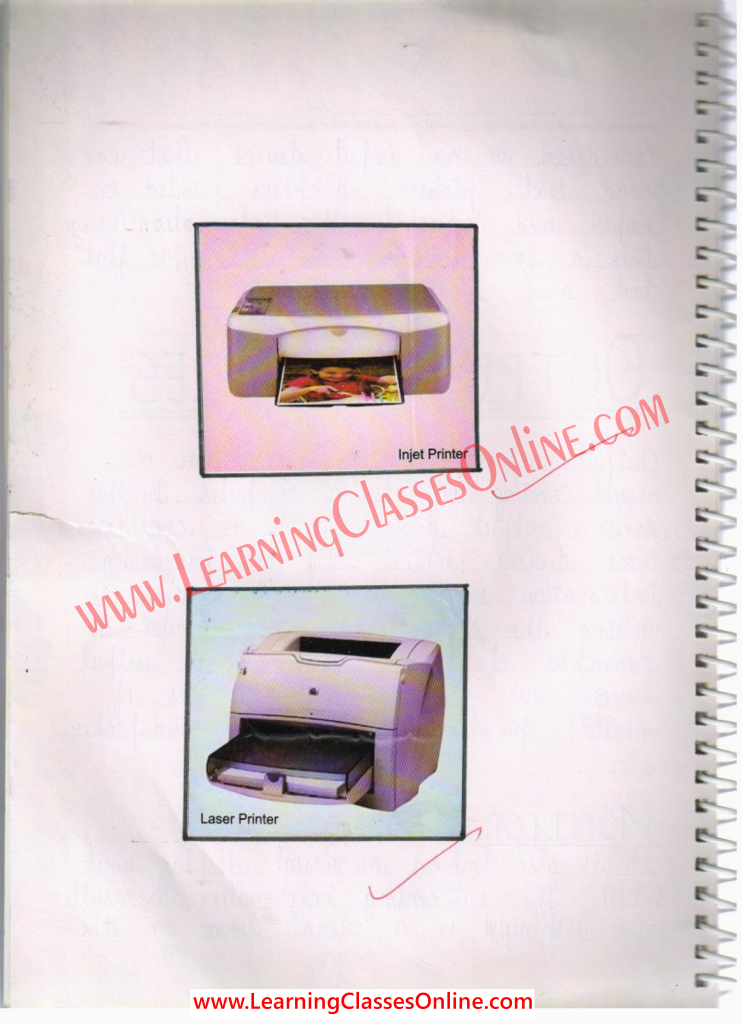
Printer :
In computing, a printer is a peripheral which produces text and/or graphics of documents stored in electronic form, usually on physical print media such as paper or transparencies. Many printers are primarily used as local peripherals and are attached by a printer cable or, in most newer printers, a USB cable to a computer that serves as a document source.
Types of Printers
- Dot Matrix printer
- Inkjet printer
- Laser printer
- Thermal printer
- LED printer
Speaker :
- A speaker is a hardware device, that is connected to a computer’s sound card, which outputs sound generated by the card.
- Audio data generated by the computer is sent to the audio card, that is located in the expansion slot.
- The card translates the data into audio signals, which are then sent to either the speakers or headphones.
- In the initial phase, computers had onboard speakers, which generated series of different tones and beeps.
- When the popularity of multimedia and computer games grew, higher-quality computer speakers came into the market.
- These new speakers were known for higher-quality sound effects and music.
Projector :
- It is a hardware device, with which an image like a computer screen is projected onto a flat-screen.
- Image data is sent to the video card, by the computer which is then translated into a video image and sent to the projector.
- A projector is often used in meetings or to make presentations, because they allow for a large image to be shown, with which the display is available for a large audience.
Plotter :
- Plotters, like printers, create a hard copy rendition of a digitally rendered design.
- The design is sent to a plotter through a graphics card and the image is created using a pen.
- In simple words, plotters basically draw an image using a series of straight lines.
- This computer output device is used with engineering applications.
Sound card :
It is Also known as a soundboard or an audio card, a sound card is an expansion card or integrated circuit that provides a computer with the ability to produce a sound that can be heard by the user either over speakers or headphones.
Video card :
Alternatively referred to as a graphics card, video board, or video controller, a video adapter is an internal circuit board that allows a display device such as a monitor to display images from the computer.
3. Memory Unit:
A data storage device is a device for recording (storing) information (data).
Recording can be done using virtually any form of energy, spanning from manual muscle power in handwriting, to acoustic vibrations in phonographic recording, to electromagnetic energy modulating magnetic tape and optical discs.
A storage device is a hardware device capable of storing information. There are two types of storage devices used in computers; a primary storage device such as computer RAM and a secondary storage device such as a computer hard disk drive.
Hierarchy of Storage
Primary Storage :
Primary storage (or main memory or internal memory), often referred to simply as memory, is the only one directly accessible to the CPU. The CPU continuously reads instructions stored there and executes them as required. Any data actively operated on is also stored there in a uniform manner.
1. Primary Storage Device :
- Also known as internal memory and main memory, primary storage is a storage location that holds a memory for short periods of time while the computer is on.
- For example, computer RAM and cache are both examples of primary storage devices.
This type of storage is the fastest type of memory in your computer and is used to store data while it's being used. For example, when you open a program data is moved from the secondary storage into the primary storage.
2. Random Access Memory :
RAM, also known as main memory or system memory, is a term commonly used to describe the memory within a computer. Unlike ROM, RAM is a volatile memory and requires power; if power is lost, all data is also lost.
Secondary storage device:
Also known as external memory and auxiliary storage, secondary storage is a storage medium that holds information until it is deleted or overwritten regardless if the computer has power.
For example, a floppy disk drive and a hard disk drive are both good examples of secondary storage devices.
1. Floppy Disk Drive :
- A Floppy Disk Drive, or FDD for short, is a computer disk drive that enables a user to easily save data to removable diskettes.
- Although 8" disk drives made available in 1971 were the first real disk drives, the first widely used floppy disk drives were the 5 1/4" floppy disk drives, which were later replaced with 3 1/2" floppy disk drives.
- However, today because of the limited capacity and reliability of floppy diskettes many computers no longer come equipped with floppy disk drives and are being replaced with CD-R and other writable disc drives and flash drives.
2. Hard drive :
The computer's main storage media device used to permanently store all data on the computer. Also referred to as a hard disk drive or abbreviated as HD or HDD, the hard drive was first introduced on September 13, 1956, and consists of one or more hard disk platters inside of air-sealed casing.
Most hard drives are permanently stored in an internal drive bay at the front of the computer and are connected with either ATA, SCSI, or a SATA cable and power cable.
Below is an illustration of the inside of a hard disk drive.
- Magnetic Tape
- Diskettes
- Compact Disc
- Digital Versatile Disc
- USB Flash Drives
Microsoft Office
Microsoft Office is an office suite of interrelated desktop applications, servers, and services for the Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X operating systems, introduced by Microsoft in 1989.
Initially, a marketing term for a bundled set of applications, the first version of Office contained Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, and Microsoft PowerPoint. Additionally, a "Pro" (Professional) version of Office included Microsoft Access and Schedule Plus.
Over the years, Office applications have grown substantially closer with shared features such as a common spell checker, OLE data integration, and Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications scripting language. Microsoft also positions Office as a development platform for line-of-business software under the Office Business Applications (OBA) brand.
THERE ARE THREE MAIN COMPONENTS IN MS OFFICE
- MS WORD
- MS POWERPOINT
- MS EXCEL
MICROSOFT WORD
Word is an application program that allows you to create and type letters, reports, memos, proposals, newsletters, brochures, graphic presentations, web pages, tables, from letters-virtually all communication required in today’s businesses.
MS-WORD for Windows is a What You See Is What You Get program which means that the user can see all fonts and graphics on the screen exactly as they will print out. Word for Windows has the ability to create graphics and graphs, Which can be added to the document.
It also makes it easy to combine text and graphics together and allows to control the appearances of text and graphics by simply clicking on the mouse. The complex command need not be remembered as all commands are displayed in a menu.
Text created from other programs like a word processors, spreadsheets, and databases can also be brought into Word for Windows with ease as there are already built-in conversion filters in it.
FEATURES OF MICROSOFT WORD
Some of the important features of Ms-Word are listed below:
- Using the word you can create the document and edit them later, as and when required, by adding more text, modifying the existing text, deleting/moving some part of it.
- Changing the size of the margins can reformat the complete document or part of the text.
- Font size and type of fonts can also be changed. Page numbers and Header and Footer can be included.
- Spelling can be checked and corrections can be made automatically in the entire document. Word count and other statistics can be generated.
- Text can be formatted in columnar style as we see in the newspaper. Text boxes can be made.
- Tables can be made and included in the text.
- Word also allows the user to mix the graphical pictures with the text. Graphical pictures can either be created in the world itself or can be imported from outside like from Clip Art Gallery.
- Word also provides the mail-merge facility.
Components of ms word:
- Insertion point: - It is a blinking vertical cursor that indicates the position on the screen where the text or graphic will be inserted.
- Workspace:- It is the area in the document window where the text is typed.
- Vertical scroll bar: - It is used to move a document vertically.
- View buttons: - They allow you to view a document in different layouts.
- Horizontal scroll bar: - It is used to move documents horizontally.
- Menu bar
As you click any word on the menu bar, a drop-down list appears, outlining all related tasks that can be performed under that heading. There are different menu bars in our ms word:
- Home menu
- Insert menu
- Page layout menu
- References menu
- Mailings menu
- Review menu
- View menu
HOME MENU:
It includes the following functions:-
- Cut: Removes the selection from the active document and places it on the clipboard.
- Copy: To copy the selected text
- Paste: This command is used only if you have cut or copied an object, text, or contents of a cell.
- Font type: This command is used to change font type
- Font size This command is used to change the font size.
- Text alignments: left, center, and right alignments.
INSERT
It includes the following functions:
- Break Inserts a page break, column break, or section break at the insertion point.
- Text Box Draws a text box with horizontal text direction where you click or drag. Text boxes help you arrange text and add text to graphics.
- Page Numbers Inserts page numbers that automatically update when you add or delete pages.
- Date and Time Add the date and time to the document using the format you choose.
- The picture adds a picture to the document from a file.
- Symbol Inserts symbols and special characters from the fonts that are installed on your computer.
- Header & footer it shows the header & footer area on a toolbar.
PAGE LAYOUT
It includes the following function:
- Margins select the margin size for the entire document or current section.
- Orientation switches the page between portrait and landscape.
- Columns split the text into two or more columns.
- Watermarks insert ghosted text behind the content on the page.
- Page borders insert or change borders around the page.
- Indent to change the left and right spacing of the paragraph.
- Spacing to change the spacing in paragraphs.
REFERENCES
It includes the following functions:-
- Table of content to add in a table of content to the document
- Add text add the current paragraph to the table of content.
- Footnote to add a footnote to the document.
- Endnote to add an endnote to the document.
MAILINGS
It includes the following functions: -
- Envelopes to create and print envelopes.
- Labels to create and print labels.
- Start mail merge used to start mail merge which one intends to print or mail multiple times.
- Select recipients to choose a list of people whom one intends to send the letter.
REVIEW
It includes the following functions: -
- Spelling and grammar Check the active document for possible spelling, grammar, and writing style errors, and displays suggestions for correcting them
- Translate to translate the selected text into a different language.
- New comment to add a comment about the selection.
- Track changes to track all changes to the document including deletion, insertion, and formatting changes.
- Compare to compare or combine multiple versions of documents.
- Protect documents restrict how people access the document.
VIEW
It includes the following functions:-
- Print layout views the document as it will appear on the printed page.
- Web layout views the document as it would look like a web page.
- Ruler to view the rulers
- Thumbnails to open the thumbnail pane which one can use to navigate a long document through small pictures of each page.
- Zoom to open the zoom dialogue box to specify the zoom level of the document
- View side by side to view two documents side by side so that one can compare their contents.
FORMAT
- Crop to crop the selected object to remove any unwanted part.
- Brightness to increase or decrease the brightness of a picture.
- Recolor to recolor the picture to give it a stylish effect.
- Compress picture in a document to reduce its size
- Reset picture to discard all formatting changes made to a picture.
- Shadow to add a shadow effect to the shape.
- Position to position the selected object on the page.
- Rotate to rotate or flip the selected object.
TABLE IN MS WORD
A table is any information grouped together, arranged in rows and columns. A table can be useful for enhancing the presentation of data in our document. we can create a table with the help of ms word. The table facility in the word is very powerful and flexible. Our table can have any number of rows and columns.
MICROSOFT POWERPOINT
- PowerPoint is a tool you can use to communicate your ideas through visual aids that appear professionally designed yet are easy to produce.
- With Powerpoint you can create a variety of media, including black and white overheads, color overheads, 35- mm slides, and an on-screen electronic slide show.
- In addition, you can prepare speaker’s notes and print outlines and handouts for your audience. All these components integrated into one file make up a PowerPoint Presentation.
FEATURES OF MICROSOFT POWERPOINT
- Quick and easy, high-impact visuals: PowerPoint ‘s Auto Content and Pick a Look wizards and templates not only help to design a presentation, but also gives a basic presentation outline to follow.
- Fact-filled presentation with plenty of graphs and charts: Power-Point’s Graph, organization chart and Table modules can help to create elaborate visuals that depict Numeric information, detail the structure of an organization and make comparisons among ideas.
- You can assemble existing text and graphics from the Microsoft office application: PowerPoint can easily integrate text, graphs, numbers, and diagrams materials. With OLE, you can edit and object within PowerPoint that you can create in another application.
- Powerpoint is a popular presentation design program that provides a complete and easy way to create a presentation to fit any need. Using Microsoft PowerPoint, we can create visually appealing presentations quickly and easily.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF VIEWS IN POWERPOINT
Slide View:
You must be working in slide view to edit text, images, or colors on the slides.
Outline View:
In outline you can quickly scan the entire presentation, edit text, but not the color of text, or do a spell check. You could also print the outline view to keep for speaker's notes as you present your show.
Slide Sorter View:
From this view you can move, copy and paste a slide and make duplicate slide.
MICROSOFT EXCEL
WORKBOOK AND WORKSHEET:
When you open Excel, the Excel application window opens with a new Excel workbook. A workbook is a multi-page Excel document. Each page in the workbook is called a Worksheet.
Row and column:
Each worksheet is divided into columns and rows. The horizontal divisions are known as row and vertical ones are known as column. They are separated by gridlines.
Cells:
A cell is a point where the row and the column intersect. For example, cell a1 is the intersection of column a and row 1. A collection of these cells is called a worksheet.
Active cell:
When a cell is active, you can type data in it. The active cell has a dark outline.
Sheet tabs:
Excel allows you to have multiple worksheets stored in a single File. The first worksheet is designated as “sheet 1” while the Second as “sheet 2” and so on.
Entering data in the worksheet:
- Click the cell where you want to enter data.
- Type the data and press enter or tab.
CREATING CHARTS IN MS-EXCEL
- To create a chart in Excel, you start by entering the data for the chart on a worksheet (worksheet: The primary document that you use in Excel to store and work with data. Also called a spreadsheet. A worksheet consists of cells that are organized into columns and rows; a worksheet is always stored in a workbook.).
- The data can be arranged in rows or columns — Excel automatically determines the best way to plot the data in the chart. Some chart types (such as pie and bubble charts) require a specific data arrangement.
- Once you have entered the data for your chart, you can select the chart type that you want to use on the Office Fluent Ribbon (Insert tab, Charts group)
INTERNET
Internet is the short name or abbreviation for the internetwork system. Internet is known as the largest WAN in the existing today.
Accordingly, it may be defined as the world’s largest internetwork system that may provide the fastest, easiest, and cheapest means for countless users to get and provide information as well as communicate among themselves on a global basis.
Internet may be considered as a name for a fast World Wide System consisting of people, information, and computers, capable of communicating and sharing data among the indefinite number of users at a time scattered all over the world.
Internet may be defined as a network of networks that are:
- Interconnected physically
- Capable of communicating and sharing data with each other
- Able to act together as a single network
This great game on the Internet can be played only with the help of two types of computer programs (software)- Servers and Clients.
Servers are programs that provide resources and the Clients are programs that we use to access those resources.
History of Internet
- ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network) laid the foundation of today’s Internet almost three decades ago.
It was established to test the security of a network.
In 1982, TCP/IP became the protocol suite for ARPANET and led to one of the first references to an “Internet” of connected networks.
NSFNET (National Science Foundation network), known as the backbone of the Internet came into existence in 1986 and until1995 NSFNET was operated by ANS (Advanced Network & Services) a research-oriented nonprofit company set up by Merit Network, IBM (International Business Machines Organisation) and MCI (Microwave Communication Inc.) in 1990 under a co-operative agreement between NSF and Merit.
When this contracted after 1995, the running and maintaining of the backbones have been taking over by Internet service providers like America Online, MCI, and Spirit in the United States. On an overall basis, IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) represented by the government and academic organizations largely governs the Internet.
Application of Internet
Internet is playing a very important role in National Development by extending the following major benefits to the citizens worldwide:
- Education
- Publishing
- Shopping
- Advertising
- Financial services
- Government and Regulations
- Careers
Some other applications of the Internet are given below:
1. Electronic Journals and News Letters:
There are hundreds of electronic journals and newsletters on the Internet. These journals are like printed counterparts in that they appear on a regular schedule, have a team of editors and reviewers, and focus on a specific topic.
2. Customization:
Information can be maintained centrally on a network server and still be displayed, accessed, and disseminated on an individual basis.Coordination: Access to shared data, project coordination, and coordinated information management resulting in an enhanced opportunity for joint development and innovative products and services.
3. Integration:
We can link online activities with internal, back-end processes for maximum impact, distribute information and customer interactions across functions and promote new business applications.
4. E-Commerce:
Internet offers Electronic Commerce (E-Commerce) which supports online ordering, purchase orders, inventory, and delivery tracking.
5. Interactions:
Two-way or multi-channel communication is possible on the net. We can get immediate and focused feedback from customers and forward online customer queries to immediate appropriate internal resources so that appropriate action can be taken.
6. Discussion Lists:
There are hundreds of electronic discussion lists and conference proceedings available over the Internet. They give users direct access to scholars in disciplines they are interested in. Discussion lists give users an opportunity to ask or offer help.
Hardware and Software requirements for Internet
The minimum hardware and software required to get an Internet connection is as follows:
- Computer: All types of computers right from PC (having DOS or Windows) to Pentium and mainframes suitable for the Internet.
- Modem: It is a device that converts the digital signal from a computer into an analog one, which is suitable for transmission over a telephone line or other convenient communication channels.
- Linkage Mechanism: The following are the methods using which linkage can be established on the Internet:
- Dial-up STD Telephone
- Leased Telephone Line
- VSAT (Very Small Aperture Terminal)
- Radio-Wave Link
- Communication Software: These days modems come with all types of communication software. And if these are not supplied as a part of modem delivery, then it is either exclusively requested from the vendor or the Internet is loaded with all kinds of freeware and shareware.
Surfing Internet
Web browser:-
A web browser or Internet browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. An information resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) and maybe a web page, image, video, or another piece of content like google.com
Various types of web browser are used to access information like
- Internet explorer
- Mozila Firefox
- Internet Explorer
- Google Chrome
- Opera
E-mail i.e. electronic mail or the letter which is sent electronically started in 1970 with just a simple text facility. But as time progress, it has developed as a great communication tool with fast speed and minimal cost.
Electronic mail, commonly called email or e-mail, is a method of exchanging digital messages from an author to one or more recipients. Modern email operates across the Internet or other computer networks.
Today's email systems are based on a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept, forward, deliver and store messages. Neither the users nor their computers are required to be online simultaneously; they need to connect only briefly, typically to an email server, for as long as it takes to send or receive messages.
The general structure of E-Mail:
- Head
- To: This section of the mail contains the unique e-mail ID of the receiver of your message.
- CC: This section contains the e-mail ID of the person to whom you want to send a copy of your mail.
- BCC: This section contains the e-mail ID where your message is returned if it is not delivered to the above-mentioned ID.
- Subject: This section contains the tag line of your message and brief information about the detailed message inside the body part. It can be treated as the title of a lesson.
- File attachment: This section contains the path of the document or file which you want to attach with your message. It can be a text, audio, video, or image file as well.
- Body: This part of an E-Mail contains the original message just like a handwritten letter. It can be simple text or text with additional features like formatting, color, highlighter, and smart emoticon, etc.
- Signature: This is the part of the body but not an actual part of the message. This part is not just a ordinary signature but it is the detailed information about the sender of the message which he/she want to tell the receiver of the message like:- name, contact number, job information, designation, etc.
Out of all these parts of an E-Mail, only the TO and Body parts are essential whether the other parts are optional.
Web Search Engine
A web search engine is designed to search for information on the World Wide Web and FTP servers. The search results are generally presented in a list of results and are often called hits.
The information may consist of web pages, images, information and other types of files. Some search engines also mine data available in databases or open directories. Unlike web directories, which are maintained by human editors, search engines operate algorithmically or are a mixture of algorithmic and human input.
Popular Search Engines
- Bing
- Yahoo
HANDLING AVAILABLE EQUIPMENT
1) EPIDIASCOPE:
Epidiascope is a device with the help of which the opaque objects can be shown on the screen. It is also known as the picture-expansion device. This device is more effective than magic lantern.
The main characteristics of epidiascope are as follows:
- There is no need of making the slides in the case of epidiascope. By this device, without making the slides, small pictures, maps, pages of the books can be shown on the screen in their magnified form.
- It is known as episcope when the opaque objects are projected.
- When a slide is projected by this device, it is known as a diascope.
- With this device, the pages of any printed book can be projected without removing them from the books, such as charts, maps, photograph,s etc.
- When an artist or a teacher fails to magnify the small pictures, this epidiascope is helpful in providing them magnified form.
- The working system of epidiascope is very simple. The intense light falls on the opaque object which is reflected by a mirror at an angle of 45. Then this reflected light passes through the projection lens and a magnified picture is formed on the screen.
PRECAUTIONS:
While using the epidiascope, the following precautions must be observer:
- A proper screen should be arranged before using the epidiascope. Without screen its use is meaningless.
- Before using epidiascope, the room should be darkened. Without darkening, the images would not be clearly seen on the screen.
- There should be complete silence in the class during the use of epidiascope so that the pupils may watch everything on the screen and the teacher may ask the questions.
- The teacher should comment continuously for the clarity of objects which are being projected. This maintains the interest of the pupils and their attention remains focused.
- The size of the object to be shown in the epidiascope should be according to the epidiascope. The size of the objects should not be such that the same may not be shown through the epidiascope.
The use of epidiascope has contributed to modern education. It has contributed almost in all the subjects such as Civics, Economics, History, and Geography, etc. In America and England, such devices are used maximum. But in India, the use of such devices is limited due to financial problems.
2) OVERHEAD PROJECTOR:
Overhead projector is a very helpful teaching aid. It is quite an advanced type of teaching aid. It is used for projecting image of the transparency on the screen. This projector makes the image above the shoulders of the teacher. Therefore, it is called overhead projector. It can be used in many ways as it projects words or pictures written on transparent sheet.
- Therefore, it is a substitution for a picture, graph, chart, or chalkboard.
- In the overhead projector, a transparent sheet is placed horizontally on the top of a light source.
- This light passes through the transparent sheet and is reflected at 90-degree angle on the screen.
It is advanced form of magic lantern an epidiascope.
This device has the following characteristics.
- This device has the capacity to function in the enlightened room too. There is no need to darken the room.
- The teacher himself can operate this device.
- The object is projected above the teacher’s shoulder. Hence, the teacher can have a full view of the entire class all the time.
- In it, large slides can be used.
- In this device, changing the slides is not difficult.
- The teacher can use the screen as a blackboard.
- In this device, the slide-marking pencil can be used to mark the slide.
- After projection, these marks can be rubbed off.
- It is very easy to operate this projector. To operate this projector, it is required to push a button, place the slide at the projection point, and focus the image on the screen only.
Uses of Overhead Projector:
An overhead projector can be used for the following purposes in the teaching.
- The teacher can develop a diagram without turning back to the chalkboard in the class. In this way, he can keep an eye on the students.
- It is very helpful in a class having a larger number of students.
- In the case of chalkboard, generally, it is seen that the teacher stands in front while writing on the chalkboard, The students can not see it properly. These problems can be solved with the help of an overhead projector.
- An overhead projector helps the teacher in engaging the students in tutorial work.
- With the help of an overhead projector, a personal approach is maintained because projection material can be made by the person who uses it.
- The overhead projector makes a very image of the world and pictures.
- The Information to be presented before the students can be made easily understood with the help of an overhead projector.
- An overhead projector can be used without making the room dark.
- The projection screen can be utilized as a chalkboard. The teacher can write or draw on the transparent sheet with a pencil.
3)TAPE RECORDER:
Tape-recorder is an audio aid. With the help of tape-recorder, valuable information can be recorded and can be played whenever required. No doubt, it is expensive but now it has become very popular, It can serve many useful purposes in the teaching.
Uses of Tape Recorder
- Taps are available for good pronunciation, prose reading, poem reciting, stress, intonation, etc. The pronunciation of the students can be developed by listening to the tapes.
- Tapes are useful for creating interest in the language.
- Tape-recorder can be used for learning the spelling of words.
- The use of Tape-recorder proves very helpful in the learning of a language. The students may be provided with records of correct conversation. It may lead them to learn how to speak correctly and express their ideas clearly, logically, and forcefully.
- It can be helpful in recording the working of the various seminars and conferences organized in the institution.
- It may be helpful in various co-curriculum activities of the institution.
- It may be useful for the teacher to assess his own teaching work.
- It can be proved as an effective aid for the evaluation of teaching-learning program carried out in the institution.
- It may be helpful in preparing useful commentary for the display of filmstrips and slides.
- It may help in preparing recorded educational programs to be used at the right time and when required.
- It may help in learning the art and skills related to speech, conversation, lecturing, and discussion
- It can be used for learning spellings of the words. Listening to such tapes will help the students learn spellings of difficult words.
4) TELEVISION:
Television is a major audio-visual air. It appeals to both hearing and sight senses. It is the most modern type of audio-visual aid which has gain popularity in the world. The learners may see and listen to whatever is being said.
At present, television is being used for teaching purposes in many big cities of our country. It is better aid than Radio. Television has been described as the head of audio-visual aids. It has become powerful mean of communication throughout the world.
Uses of Television:
Television can be used of the following purposes in the teaching.- With the help of television, a large number of students can be given information at a time.
- It is helpful in improving the pronunciation of the students.
- It develops the skills of listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
- Television is an important means to non-formal education that is distance education or open learning.
- It attracts the attention of the students and maintains their interest in learning.
- Teaching by the talented teachers through television is helpful in enhancing the quality of education.
- The most difficult topics like phonology, morphology, and syllabus can be taught more easily through television.
- The lessons can be made more easily understandable through acting and dramatization with the help of Television.
- It provides the facility to those students who are unable to attend the class due to some reasons.
- Television provides equal opportunities to all the students to get an education through its programs. Rural students also can get benefits from this aid. In this way, high-quality education is no longer limited to big cities.
- Television is a time-saving device. The syllabus may be covered in less time because everything in the lesson is planned carefully without any sort of deviation.
- The solution to different problems related to education can be easily made with the help of educational programs on Television.
5) VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER:
The videocassette recorder is a type of video tape recorder that uses video removable videotape cassettes containing magnetic tape to record audio and video fro a television broadcast so it can be played back later. Most VCRs have their own runner (for direct TV reception) and a programmable timer (for unattended recording of a certain channel at a particular time).
Uses of Video Tape-Recorder:
- It can be useful for creating interest in the language.
- It can be used for learning the spelling of words.
- The use of VCR proves very helpful in the learning of a language. The students may be provided with records of correct conversation. It may lead them to learn how to speak correctly and express their ideas clearly, logically, and forcefully.
- It can be helpful in recording the working of the various seminars and conferences organized in the institutions.
- It may be helpful in various co-curriculum activities of the institution.
- It may be useful for the teacher to assess his own teaching work.
- It can be proved as an effective aid for the evaluation of teaching-learning program carried out in the institution.
- It may help in preparing recorded educational programs to be used at the right time and when required.
- It may also help in learning the art and skills relate to speech, conversation, lecturing, and discussion.
6) SLIDE PROJECTOR:
A slide projector is an opto-mechanical device to view photographic slides. It has four main elements: a fan-cooled electric light bulb or other light source, a reflector and “condensing” lens to direct the light to the slide, a holder for the slide and a focusing lens.
A flat piece of heat absorbing glass is often place in the light path between the condensing lens and the slide, to avoid damaging the latter. The glass transmits visible wavelengths but absorbs infrared. Light passes through the transparent slide and lens, and the resulting image is enlarged and projected onto a perpendicular flat screen so the audience can view its reflection.
Alternatively, the image may be projected onto a translucent “rear projection also avoids the audience’s interrupting the light stream or bumping into the projector. Slide projectors were common in the 1950s and 1960s as a form of entertainment; family members and friends would gather to view slideshows.
In-home photographic slides and slide projectors have largely been replaced by low-cost paper prints, digital cameras, DVD media, video display monitors, and digital projectors. As of October 2004, Kodak no longer manufactures slide projectors. It is increasingly difficult in some countries to locate photo processors who will process slide film.
Type of projector:
- Carousel slide projectors (includes tray-style projectors)
- Dual slide projectors
- Single slide projectors(manual form)
- Viewer slide projectors
- Slide Cube projectors
- Stereo slide projectors(projects two slides simultaneously with different)
Uses of slide projector:
- Many concrete ideas can be concretized with the help of slides. These help in making teaching clear, interesting, and intelligible.
- With the help of SP, small things can be shown in big form and shape.
- Children are attracted to pictures by nature. These can develop children’s interests in teaching-learning process.
- Their use brings variety in teaching.
- The sequence of events seen through slides is retained by the students for a longer period of time in there.
SMART CLASSROOM
Smart class is a modern and smart class using multimedia, Internet & e-learning devices in classroom teaching. These classes are something different from traditional classes because traditional classes use traditional teaching-learning devices.
- A smart classroom is a “Whiteboard classroom”, using whiteboard (Projector), computers and multimedia in classroom teaching-learning. In the future we may hear some new words for our classroom; such as “Digiclass”, whiteboard classroom, or e based classroom.” Smart class” is a modernized method of teaching-learning techniques.
- Our education is going to be modernized and is going to be using “Interactive whiteboard teaching-learning techniques in schools”.
Quality education is an essential requisite in today's competitive environment. Technology has affected us in every aspect. Smart classes as a modernized method of education in Indian education scenario which provides quality education to students by helping them in better concept formation, concept elaboration, improvement in reading skills, and academic achievement.
There has been a lot of buzz about this technology. The smart class was launched by EDUCOM in 2004. It was developed around the ideology that for technology to become an integral part of day-to-day teaching and learning practices in schools, it needs to move right into the classrooms where the students and teachers spend 80% of their time.
It has been now adopted by 1000 schools across India and helps in a rapid transformation of moving technology into classrooms in India. (Corporate Diary,2007)
BENEFITS OF SMART CLASSROOMS:
- Introduction Of concept in a thrilling and exciting manner.
- A student‘s better engagement with the content and a smartboard are dynamic and visually more appealing.
- Storage of teachers' written notes.
- Voice recording is possible.
- Teaching skills can be enhanced by showing various videos to the students.
- Scope for the integration of different types of technology and other novel ways for the teachers to present lessons.
- Educomp smart class brings about a complete transformation in classrooms. This results in a faster and accurate understanding of the concepts in class and helps improve the overall academic performance of students.
- Teachers are able to keep students engaged in the learning process and also get an instant and accurate assessment of learning outcomes achieved at the end of the class.
Smart classroom Equipment:
As a teacher or even a presenter, one comes across a variety of problems while delivering lectures, discourses, seminars or presentations, etc. These issues are numerous and basically stem when there’s a failure in meeting out an organized course or study material and data to the audience. To cope up with such problems and situations a person has to guarantee that certain things be carried out.
Here’s a list of some important items you need in order to set up a smart classroom:
- A desktop or laptop acting as a central system.
- Document camera/Visualisers
- Projector
- Camera
- CD/DVD player
- Graphic tablets
- Remote controls
- Big Interactive LED/LCD Panels
- Interactive Whiteboard
- Multimedia Pens/Stylus
(Information And Communication Technology) ICT B.Ed Practical File in Englsih Download PDF
List of The Topics Covered IN ICT (Information and Communication Technology) PDF File in English:
- Introduction To Information And Communication Technology (ICT)
- Meaning Of Information And Communication Technology
- Definition Of Information Technology
- Importance Of ICT Technology For The Students, Teacher, Counsellors, Education Administrators And Planners And Educational Researches
- Basic Concepts Of An Operating System
- Definition And Meaning Of Operating System
- Basic Features Of Operating System
- Functions Of An Operating System
- Input Devices
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Scanner
- Output Devices
- Monitor
- Printer
- Sound Card And Speakers
- Microsoft Windows
- MS Word
- Working With MS Word
- MS Excel
- Basic Terminology
- Ms-PowerPoint
- Working With Ms PowerPoint
- Internet
- Internet Access
- Multimedia
- Ms-Access
- Ms-Paint
- Conclusion
Tags:
Ict File English
Ict File In English Pdf
Ict B.Ed Practical File Free Download Pdf
Critical Understanding Of Ict In Education B.Ed 1st And 2nd Year And All Semester Practical File, Project, Assignment, Notes, Study Material, Book In English Medium Pdf
Computer Practical File In English Langauge For B.Ed Students
Computer Practical File In English
Information And Communication Technology Ict Practical File
Ict Project In English
Ict Assignment In English
Critical Undrstanding Of Ict Pdf Handmade Short Exam Notes And Book
ICT File in English for B.Ed 1st Year
List of the Topic Covered:
- Meaning and Definition of ict in English
- Use of Information And Communication Technology in English
- Importance of ict in English
- Meaning and definition of ict in English
- Generations of computer in English
- Classification of computer in English
- Features of computer in English
- Computer hardware in English
- Input devices in English
- Output devices in English
- Software and types of software in English
- Ict in English
- Ict devices in English
- Use of ict in education in English
- Barriers in implementing ict in school in English
- Computer
- Introduction
- Meaning
- Basic functions of the computer
- Classification of computer
- Micro Computer
- Mini Computer
- Main Frame Computer
- Super Computer
- Operation system
- Introduction
- How to start the computer
- Booting
- Parts of Computer
- Desktop
- Mouse
- Keyboard
- monitor
- laser printer
- inkjet printer
- Windows (Taskbar, file, desktop, folder, creating files and folders, copying file, upload/download files
- Network
- introduction,
- types of network (LAN, WAN, MAN)
- Ms- Word
- PowerPoint presentation
- Ms- excel
- Multimedia
- Internet Components
- World Wide Web (WWW)
Hello, Friends Welcome to LearningClassesOnline, Today We Have Shared the Fully Handmade Critical Understanding of ICT Practical File, Check More Details Below.
Well, It Is Very Hard To Find Critical Understanding of ICT (Information and Communication Technology) Practical File In English For B.Ed First and Second Year. Here We Have Provided the Free Practical File Of Critical Understanding of ICT in Education subjects Especially for BEd Students That You Can Download Very Easily in PDF Format.
Not Only B Ed But It Will Be Helpful to Every Teacher and Student of Any Course. This PDF File Will Provide A Lot of Help in Making Your Critical Understanding of ICT Assignments and Projects On Time. The Download Link Is Provided Below the Post.
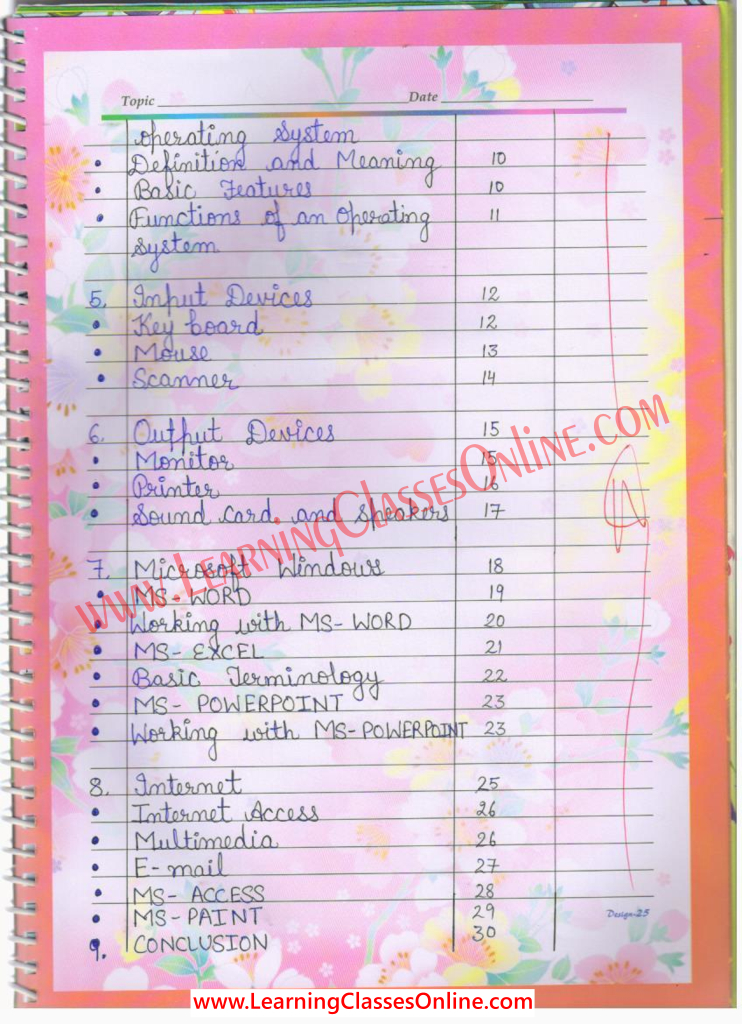
List of The Topics Covered in The Practical File
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT): Introduction, Meaning, Definition, Importance, and Uses
- Computer Basics
- Operating System
- Input and Output Devices
- Microsoft Windows
- MS Office
- Internet and Multimedia
Critical Understanding of ICT B.Ed Practical File Pics and Images


















































Similar Posts
💁Hello Friends, If You Want To Contribute To Help Other Students To Find All The Stuff At A Single Place, So Feel Free To Send Us Your Notes, Assignments, Study Material, Files, Lesson Plan, Paper, PDF Or PPT Etc. - 👉 Upload Here
अगर आप हमारे पाठकों और अन्य छात्रों की मदद करना चाहते हैं। तो बेझिझक अपने नोट्स, असाइनमेंट, अध्ययन सामग्री, फाइलें, पाठ योजना, पेपर, पीडीएफ या पीपीटी आदि हमें भेज सकते है| -👉Share Now
If You Like This Article, Then Please Share It With Your Friends Also.
Bcoz Sharing Is Caring😃




Hlo sir pls provide me sessional work of b ed course no 201 202 203 teaching in phy science and teaching in english yoga and action research
ReplyDeletePls sir it's urgent
Very useful material
ReplyDeletePost a Comment
Please Share your views and suggestions in the comment box